Ever wonder how your plastic garden hose or that clear food packaging gets made? There’s a powerful process behind these everyday items, and it’s called plastic extrusion. Used in industries ranging from construction to packaging, plastic extrusion is a core manufacturing method that transforms raw plastic into usable products.
The real beauty of this process lies in its ability to continuously produce long lengths of plastic shapes—from simple tubing to complex window frames. In this article, we’ll unravel how plastic extrusion works, the machines involved, the materials used, and why it’s such an indispensable part of modern manufacturing.
What is Plastic Extrusion?

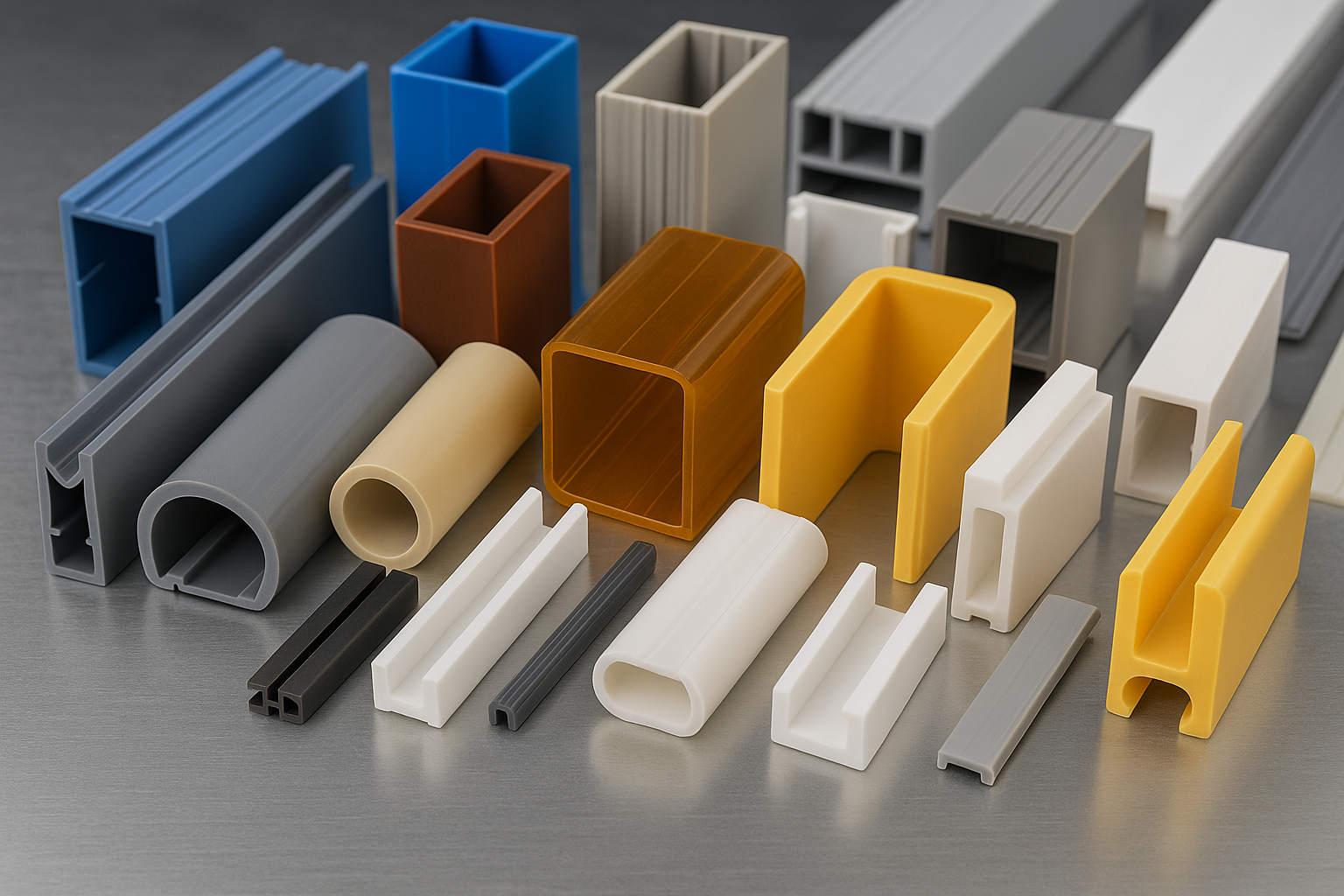
Plastic extrusion is a continuous manufacturing method where thermoplastic material is melted and formed into a profile. Think of it as “plastic spaghetti-making”—where the plastic is melted and squeezed through a mold (or die) to create items like tubing, weather stripping, and even window frames.
It’s used widely because of its versatility, speed, and ability to produce large quantities with minimal waste. The process can be tweaked to produce hollow, solid, multilayered, or foamed profiles depending on industry needs.
History of Plastic Extrusion
The roots of plastic extrusion go back to the early 20th century when thermoplastics started gaining commercial traction. In 1935, Paul Troester in Germany built the first extruder, paving the way for industrial-level plastic manufacturing. Over time, the technology evolved with advancements in polymer chemistry, automation, and die design, making it one of the most used plastic-forming processes in the world today.
Basic Principles Behind the Process
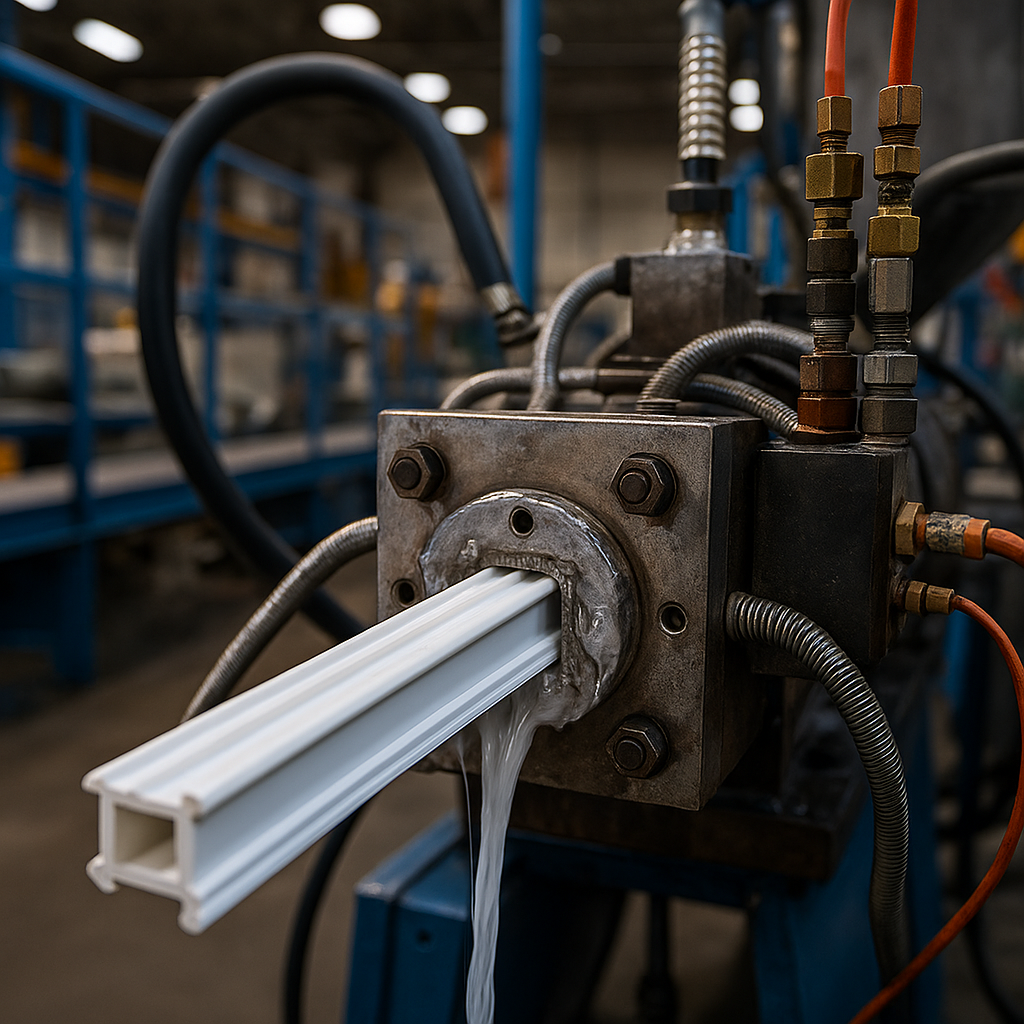
The process hinges on three principles: heat, pressure, and motion. First, raw plastic pellets are heated until they melt into a viscous fluid. Then, a rotating screw pushes this melted plastic forward through a die—a steel plate with a hole in the desired shape. As the plastic exits the die, it’s cooled and hardened into its final form.
Simple in theory, but incredibly precise in execution.
Materials Used in Plastic Extrusion
Plastic extrusion works best with thermoplastics—plastics that melt when heated and solidify when cooled. Common ones include:
- Polyethylene (PE): Used in films and plastic bags
- Polypropylene (PP): Found in automotive parts and textiles
- Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC): Used in pipes and window frames
- Polystyrene (PS): Used in packaging and insulation
- Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS): Used for durable parts like keyboard keys and LEGO bricks
Each material offers different benefits like flexibility, toughness, chemical resistance, or clarity.
Types of Plastic Extrusion
There’s more than one flavor of plastic extrusion. Here are the main types:
- Sheet Extrusion: Produces flat plastic sheets
- Film Extrusion: Makes thin plastic films, often for packaging
- Tubing Extrusion: Used for hoses and medical tubing
- Profile Extrusion: Creates complex cross-sectional shapes like window seals
- Co-extrusion: Combines multiple layers of plastics in one product
Each type addresses a unique industrial or commercial need.
How Plastic Extrusion Works: The Process Overview
Here’s a quick rundown of the process:
- Feeding: Plastic pellets are loaded into a hopper.
- Melting: The pellets travel down a heated barrel via a rotating screw.
- Pressurizing: The screw applies pressure to the melted plastic.
- Shaping: The molten plastic is forced through a die.
- Cooling: The shaped plastic is cooled using air or water.
- Cutting/Winding: The final product is cut to length or wound into rolls.
This may sound linear—and it is—but every stage is a balancing act of speed, temperature, and pressure.
The Importance of the Die
The die is arguably the most critical component of the process. Crafted with extreme precision, it determines the cross-sectional shape of the final product. From flat sheets to intricate T-profiles, the die is custom-designed for the specific application.
Die maintenance is vital. Any slight imperfection or misalignment can cause inconsistencies in the product, leading to waste or rejection.
Cooling and Sizing
Once the plastic has exited the die, it must be cooled quickly to retain its shape. Cooling methods vary based on the product:
- Air Cooling: Used for thin, delicate profiles.
- Water Cooling: Effective for larger, solid shapes like pipes.
- Vacuum Sizing: Used for complex profiles to maintain tight tolerances.
Proper cooling ensures the final product doesn’t warp, shrink, or lose its dimensional stability.
Single vs. Twin-Screw Extruders
Extrusion machines generally come in single-screw or twin-screw variants:
- Single-screw extruders are best for straightforward extrusion with one type of material.
- Twin-screw extruders excel at blending materials, incorporating additives, and improving uniformity.
If you’re dealing with recycled plastics or materials that require mixing, twin-screw systems are often the better choice.
Benefits of Plastic Extrusion
Plastic extrusion brings several advantages:
- Continuous Production: Ideal for long products or high-volume orders.
- Material Efficiency: Generates minimal waste.
- Customization: Products can be tailored by adjusting dies or materials.
- Cost-Effective: Especially for large-scale manufacturing.
It’s no wonder this process is a staple in industries from construction and automotive to electronics and packaging.
Common Applications of Extruded Plastic Products
Here’s a quick look at some real-world products made using plastic extrusion:
| Industry | Extruded Products |
| Construction | Pipes, window frames, siding |
| Medical | Tubing, catheter covers |
| Packaging | Plastic films, food wraps |
| Automotive | Weather seals, dashboard trims |
| Consumer Goods | Hoses, cable insulation, toys |
From daily essentials to high-tech applications, extrusion plays a role in shaping our world—literally.
Final Thoughts: The Future of Plastic Extrusion
Plastic extrusion is far more than a technical curiosity—it’s an essential process that powers multiple industries with efficiency, customization, and scalability. As technology evolves, we can expect to see greener materials, smarter machines, and even more innovation in how this process shapes the world.
Whether you’re in manufacturing or simply curious about how things are made, understanding how plastic extrusion works is a step toward appreciating the seamless complexity behind everyday items.
For businesses seeking reliable, high-quality plastic extrusion services, Accord Plastics is a top-tier partner known for innovation, precision, and customer-focused solutions. Reach out to their expert team today to discuss your next project or request a custom quote.
FAQs About Plastic Extrusion
What’s the main advantage of plastic extrusion?
It allows continuous production of long plastic items, making it fast and cost-effective.
Can I use recycled plastics in extrusion?
Yes, many operations successfully use post-consumer or industrial recycled materials.
Is extrusion suitable for complex shapes?
Yes, with the right die design and material, you can achieve intricate profiles.
How long does it take to set up an extrusion line?
Setup can range from a few hours to several days, depending on the complexity of the die and material.
What are the signs of poor extrusion quality?
Look out for uneven surfaces, discoloration, or inconsistent dimensions.